Excel does not have any built-in way of formatting numbers such that the numbers are displayed in a neatly readable way using SI prefixes, like m for milli (10^-3), k for kilo (10^3), µ for micro (10^-6) etc. Here I provide a VBA function I wrote to fill this need. In addition, I added support for using the prefix notation of Spice circuit simulators where both m and M are interpreted as milli and Meg has to be used to signify mega. Also, u has to be used instead of µ to indicate micro in Spice.
As icing on the cake, I also wrote a function to convert the resulting strings back to numbers.
The functions are called FormatPrefix and ValPrefix. Source code with detailed descriptions of the input arguments are shown further down in this post.
Below is a link to an Excel document with the functions built into a VBA module and a worksheet with an example table of values fed to the function to display its output for a large variation of input arguments:
![]() ExcelPrefixFormattingFunction.xls
ExcelPrefixFormattingFunction.xls
Here is a screenshot demonstrating the formatting:
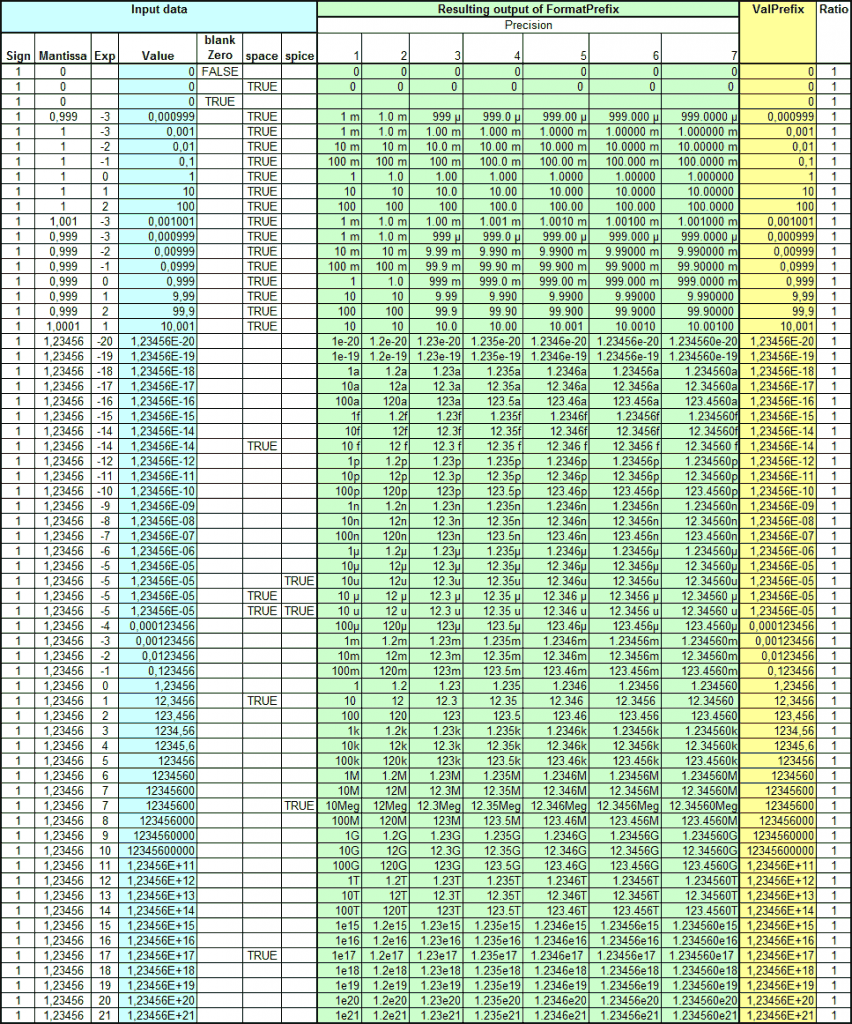
The source code is shown below:
Public Function FormatPrefix(value As Double, _ Optional precision As Integer = 3, _ Optional blankZero As Boolean = False, _ Optional space As Boolean = False, _ Optional spice As Boolean = False) As String ' Convert a number to a string, usually with an SI prefix at the end. ' ' Arguments: ' value is the value to be converted. ' Optional precision argument determines number of significant digits to be printed (default 3). ' Optional blankZero argument determines if zero should return the empty string (default false). ' Optional space argument determines if a space should be inserted after the number but before ' a possible prefix (default false). ' Optional spice argument determines if Spice prefixes should be used instead of metric ones ' (default false). The only differences are Meg vs M and u vs µ. ' Values above or equal to 1e15 or below 1e-18 are printed using scientific notation without ' prefix. ' The decimal indicator is always a point, even if the locale says it should be a comma. ' ' Written by Per Magnusson, Axotron, 2016-02-26 ' This code is public domain and comes without any warranty. Enjoy! ' Handle the value 0 If value = 0 Then If blankZero Then FormatPrefix = "" Else If space Then FormatPrefix = "0 " Else FormatPrefix = "0" End If End If Exit Function End If ' Handle negative numbers sign = 1 If value < 0 Then sign = -1 ' store the sign value = -value ' make value positive until later End If ' Calculate exponent and mantissa exponent = Int(Log(value) / Log(10#)) mantissa = Round(value / (10 ^ exponent), precision - 1) If mantissa >= 10 Then ' Handle the case where the mantissa is rounded up to 10 exponent = exponent + 1 mantissa = mantissa / 10 End If exponent3 = 3 * Int(exponent / 3) 'exponent rounded down to nearest multiple of 3 ' Find the right prefix If exponent >= 15 Then ' Too big to represent with the supported prefixes, use scientific notation prefix = "sci" ElseIf exponent >= 12 Then prefix = "T" ElseIf exponent >= 9 Then prefix = "G" ElseIf exponent >= 6 Then If spice Then prefix = "Meg" Else prefix = "M" End If ElseIf exponent >= 3 Then prefix = "k" ElseIf exponent >= 0 Then prefix = "" ElseIf exponent >= -3 Then prefix = "m" ElseIf exponent >= -6 Then If spice Then prefix = "u" Else prefix = "µ" End If ElseIf exponent >= -9 Then prefix = "n" ElseIf exponent >= -12 Then prefix = "p" ElseIf exponent >= -15 Then prefix = "f" ElseIf exponent >= -18 Then prefix = "a" Else ' Too small to represent with the supported prefixes, use scientific notation prefix = "sci" End If If prefix = "sci" Then ' Use scientific notation formatStr = "0" If precision > 1 Then formatStr = formatStr & "." For ii = 1 To precision - 1 formatStr = formatStr & "0" Next End If formatStr = formatStr & "e-0" prefix = "" value = sign * mantissa * 10 ^ exponent Else decimals = precision - (exponent - exponent3) - 1 If decimals > 0 Then formatStr = "0." For ii = 1 To decimals formatStr = formatStr & "0" Next Else formatStr = "0" End If value = sign * mantissa * 10 ^ (exponent - exponent3) End If optSpace = "" If space Then optSpace = " " End If FormatPrefix = Replace(Format(value, formatStr) & optSpace & prefix, ",", ".") 'FormatPrefix = formatStr & optSpace & prefix End Function Public Function ValPrefix(str As String) As Double ' Convert a number formatted as a string using FormatPrefix() back to a number. ' ' Arguments: ' str is the string to be converted ' Error checking is very limited. ' ' Written by Per Magnusson, Axotron, 2016-02-26 ' This code is public domain and comes without any warranty. Enjoy! exponent = 0 prefix = "" strlen = Len(str) If StrComp(Right(str, 1), "A") >= 0 Then ' There is a letter at the end of the value ii = 1 While StrComp(Mid(str, strlen - ii, 1), "A") >= 0 ii = ii + 1 Wend prefix = Mid(str, strlen - ii + 1) Select Case prefix Case "T" exponent = 12 Case "G" exponent = 9 Case "M" exponent = 6 Case "Meg" exponent = 6 Case "k" exponent = 3 Case "m" exponent = -3 Case "u" exponent = -6 Case "µ" exponent = -6 Case "n" exponent = -9 Case "p" exponent = -12 Case "f" exponent = -15 Case "a" exponent = -18 Case Else ' Error, handle it somehow? ValPrefix = "Prefix error" Exit Function End Select End If ValPrefix = Val(str) * 10 ^ exponent End Function
Hi,
The ExcelPrefixFormattingFunction.xls is not available.
Can you verify please.
Thank you.
Hi Stéphane,
Thanks for pointing that out. I have corrected the link, so it should work now.
Per
Many Thanks for your work!