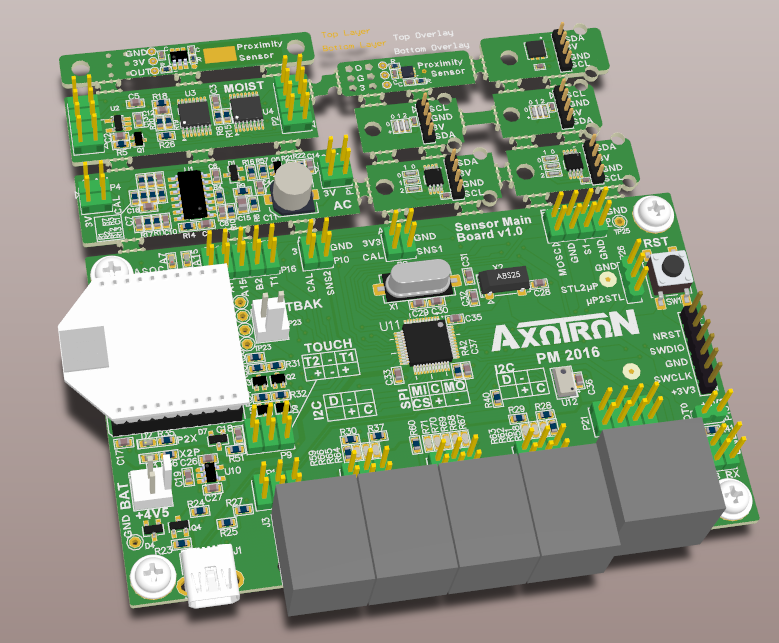
The PCB I mentioned in the previous post was rejected by the Chinese manufacturer I sent it to since it contained several sub-boards and they wanted (a lot of) extra money for that. This is what the board looked like:
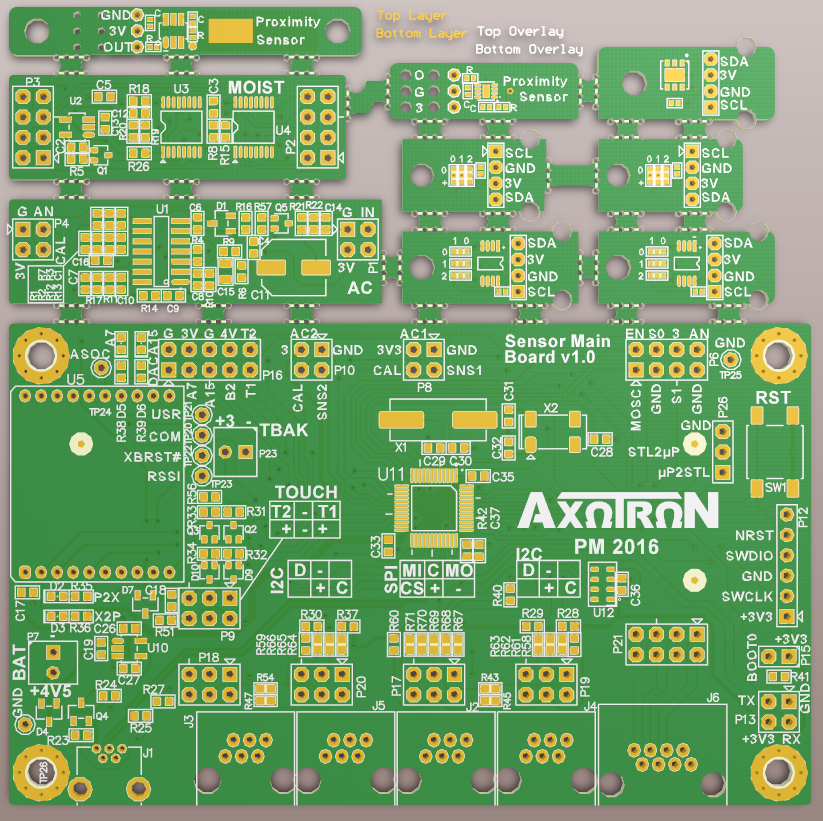
The comment I got was:
“After checked, we found there are 10 separated sub-boards in your Gerber file, it means you should pay extra $81 for it. If you don’t want to pay extra money, you can design a big outline like below right picture, then we will manufacture your boards according to your big outline.”
This is the picture they sent:
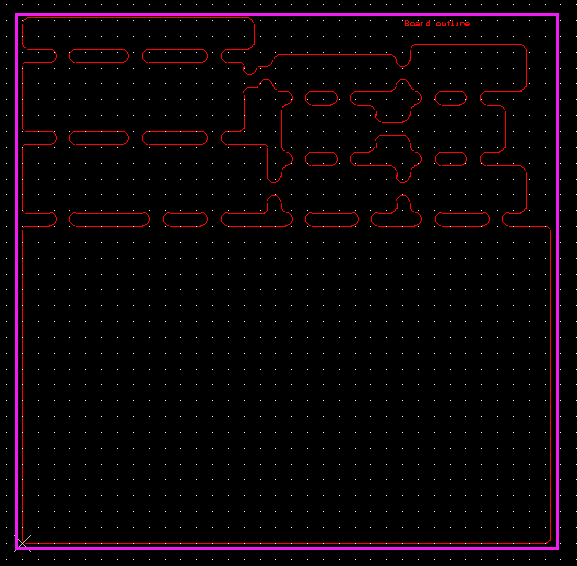
The manufacturing of ten pieces of a 10 cm x 10 cm board costs $11.90 (plus shipment), so paying an extra $81 just because I used the space to fit several smaller boards did not seem reasonable to me. The suggestion of changing the outline to avoid this cost looked like a more attractive solution, but the square outline suggested would mean I would have a rather painful depanelization to perform, so it did not look ideal.
I checked several other Chinese PCB manufacturing sites (a reasonable list can be found at the EEVblog) but all had these odd and relatively high extra fees for placing several designs within the available area. I wonder why they all have the same rules?
So what I ended up trying was to change the panelization such that it was somewhat less obvious, but with an outline that would still help me depanelize the individual boards. I removed the internal milling and the mouse bites. Then I changed the total outline to meander around larger parts of the outline of several of the smaller boards:
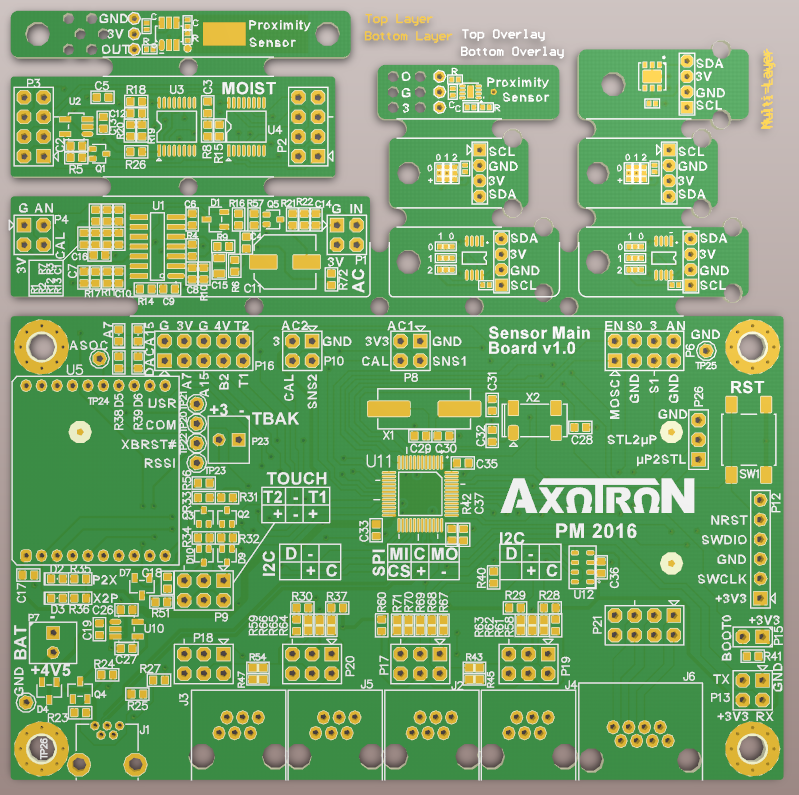
This apparently was acceptable since I got the following response:
Yes, this Gerber file is acceptable to us. We will manufacture your boards according to your new Gerber file.
About the separated sub-boards, you can refer to below requirement.If the milling part more than 1/3, it will be counted as the separated sub boards, because it is more difficult than normal single board.
For example, 10cm length boards:
the milling length is 3cm or less, no separated sub-board.
the milling length is 3.3cm or more, separated sub-board.
So it seems like as long as one stays away from having more narrow necks than 2/3 of the width of the board, one will avoid the extra cost. I actually do not think I quite obeyed this rule in the modified version of the board, but apparently it was accepted, so either they are not very strict, or the rules they apply are more complicated than what they say.